Can Hearing Loss Be Reversed? And What to Know About Hearing Loss in One Ear
Hearing loss is one of the most common health concerns in the UK, but it’s also one of the most confusing. People often ask:
“Can hearing loss be reversed?”
“What causes hearing loss in one ear?”
“Can hearing loss cause dementia or balance problems?”
“Can hearing loss in one ear be cured?”
These are not just medical questions, they are questions about quality of life. In this blog, we’ll explore both: when hearing loss can be reversed and what it means if you only experience hearing loss in one ear.
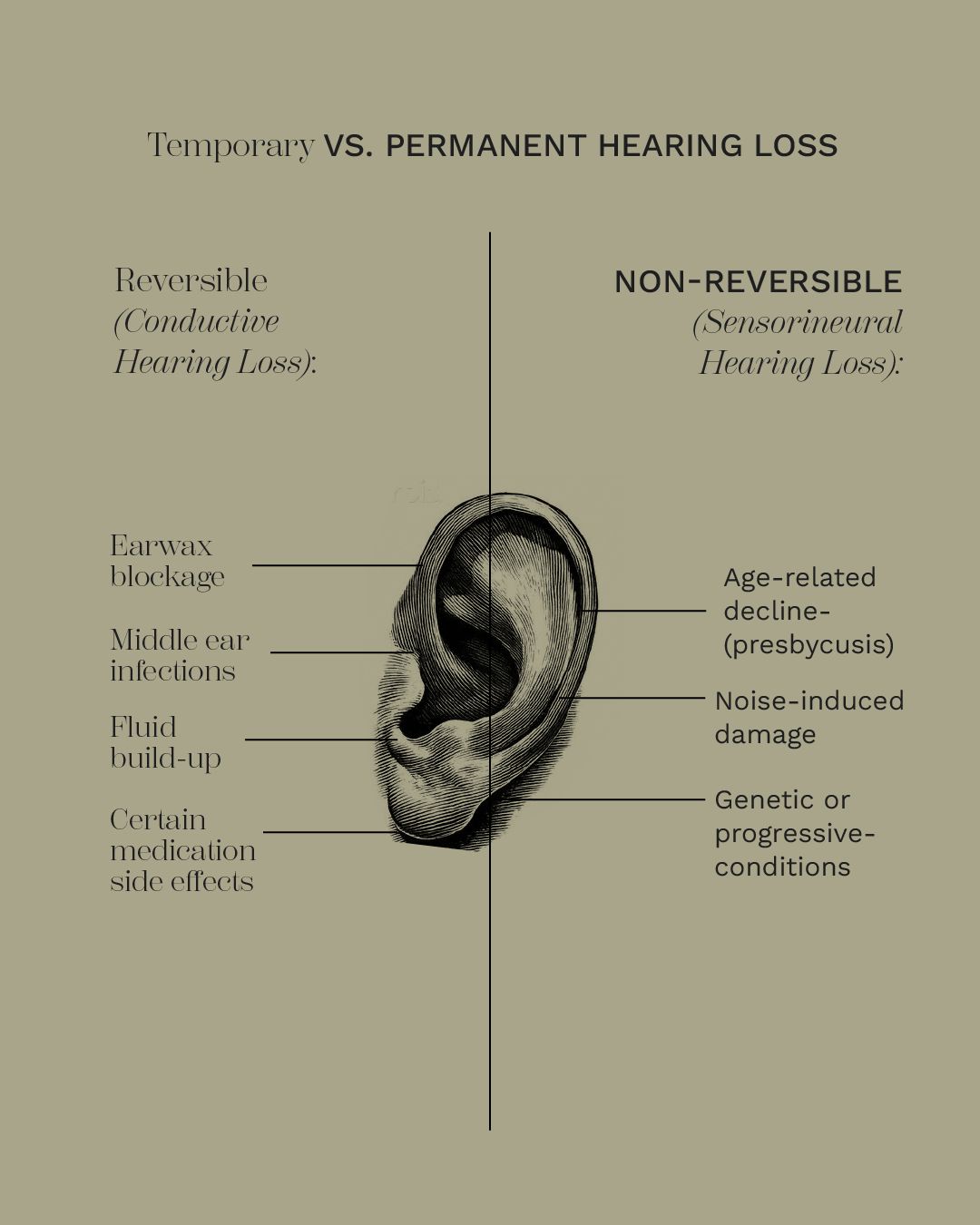
Temporary vs. Permanent Hearing Loss
Reversible (Conductive Hearing Loss):
Earwax blockage
Middle ear infections
Fluid build-up
Certain medication side effects
Non-Reversible (Sensorineural Hearing Loss):
Age-related decline (presbycusis)
Noise-induced damage
Genetic or progressive conditions
Mixed Hearing Loss: A combination of both types, where some elements can be treated but others require long-term management.
Wider Health Connections
Hearing Loss and Dementia
Research shows untreated hearing loss is strongly linked with an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia. Difficulty hearing reduces brain stimulation, increases mental load, and may lead to social withdrawal.
Hearing Loss and Balance
The inner ear plays a crucial role in balance. Hearing loss, particularly when linked to inner ear conditions, can contribute to dizziness and instability.
Hearing Loss and Tinnitus
Many people with tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ears) also experience hearing loss. Treating hearing loss with hearing aids or therapies can often reduce tinnitus symptoms.
Hearing Loss and Mental Wellbeing
Untreated hearing loss can cause frustration, isolation, anxiety, and depression. Addressing it restores confidence and connection.
Treatment Options at The Well Being By Cubex
Comprehensive Hearing Assessments: the first step to identify the type and cause.
Medical Treatments: antibiotics for infections, microsuction for earwax, surgery in rare cases.
Advanced Hearing Aids: discreet, modern devices with features like noise reduction and Bluetooth connectivity.
Tinnitus and CALM Programme: combining audiology with mindfulness and stress reduction.
Lifestyle Care: noise protection, mindfulness, and nutritional support for cognitive health.
Hearing Loss in One Ear (Unilateral Hearing Loss)
“Hearing loss in one ear” is one of the most common search topics related to hearing. It can be sudden, gradual, temporary, or permanent.
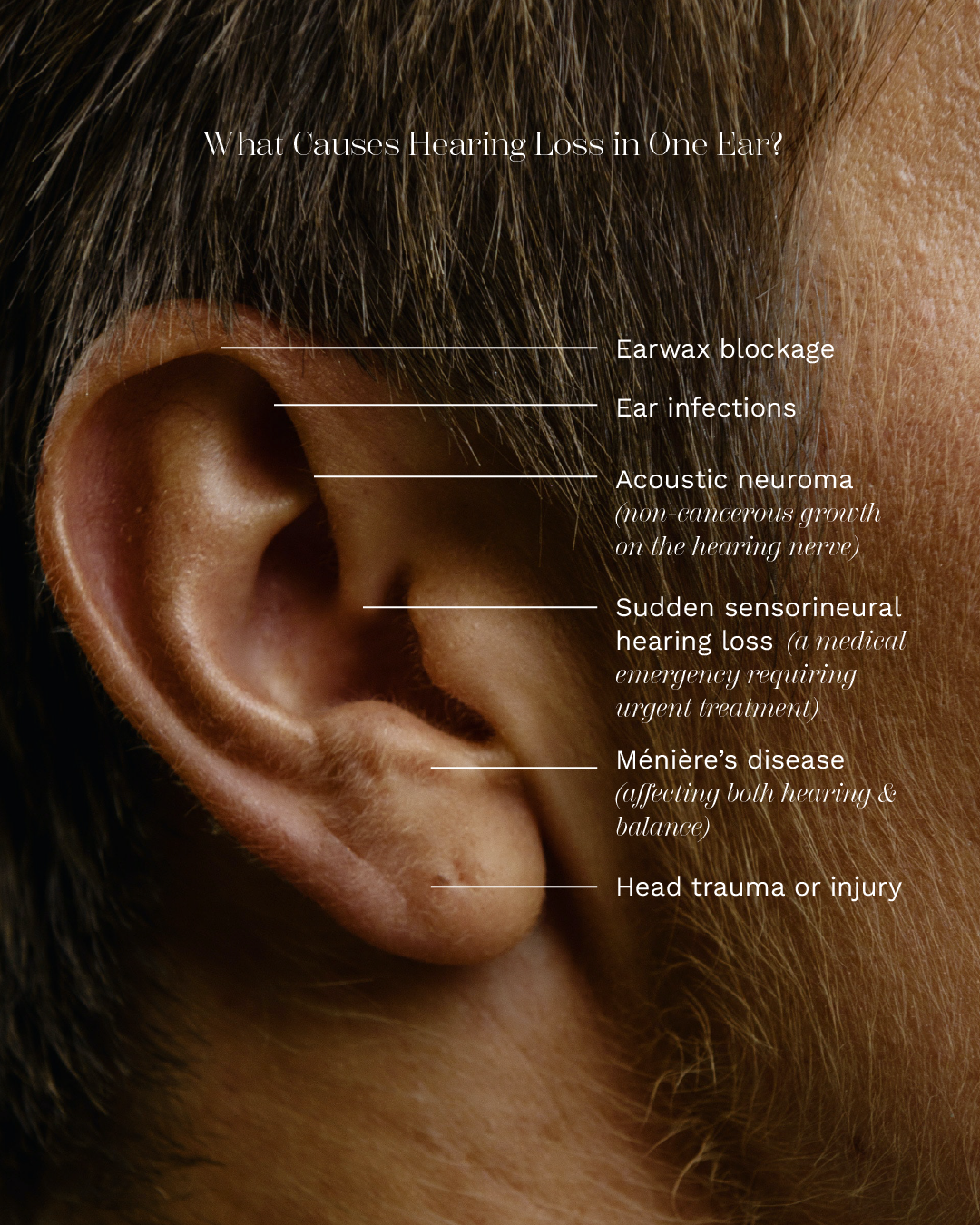
What Causes Hearing Loss in One Ear?
Earwax blockage
Ear infections
Acoustic neuroma (non-cancerous growth on the hearing nerve)
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (a medical emergency requiring urgent treatment)
Ménière’s disease (affecting both hearing and balance)
Head trauma or injury
Symptoms to Watch Out For
Difficulty locating sounds
Asking people to repeat themselves, especially on one side
Tinnitus in the affected ear
Feeling off-balance
Sounds seeming muffled or distorted on one side
Why Early Diagnosis Matters
Unilateral hearing loss should never be ignored. Some causes, such as sudden sensorineural hearing loss or acoustic neuroma, require immediate attention. The earlier the intervention, the better the outcome.
Living Well With Hearing Loss
Even if hearing loss isn’t reversible, it doesn’t have to hold you back. Many clients at The Well Being By Cubex regain confidence, improve communication, and enhance wellbeing through tailored care.
-
Yes, especially if related to inner ear conditions.
-
It depends on the cause: wax removal, medication, steroids, or hearing devices.
-
No. Conductive types can often be treated, while sensorineural types are usually permanent.
-
Untreated hearing loss increases dementia risk. Managing it helps protect long-term brain health.
-
This may be sudden sensorineural hearing loss, which needs urgent medical help within 72 hours.
Conclusion & Call to Action
So, can hearing loss be reversed? Sometimes. And what about hearing loss in one ear? Sometimes it’s temporary, but it can also be a warning sign of something more serious.
The only way to know for sure is with a comprehensive hearing test.
👉Take control of your hearing health.